New Delhi: In the realm of health and fitness, understanding one’s body composition is key to maintaining overall well-being. One of the most commonly used tools for this purpose is the Body Mass Index (BMI) calculator.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about BMI, its significance for women’s health, and its relevance in the context of health insurance. The BMI calculator is a valuable tool for women to assess their weight status and associated health risks.
What is BMI?
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a measure of body fat based on a person’s weight and height. It provides a simple numeric value that helps categorize individuals into different weight status categories.
Understanding BMI for Women’s Health
BMI is particularly important for women as it offers insights into potential health risks associated with weight. Maintaining a healthy BMI is crucial for preventing various health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers, which can disproportionately affect women.
How to Calculate BMI for Women?
Calculating BMI is straightforward and can be done using the following formula:
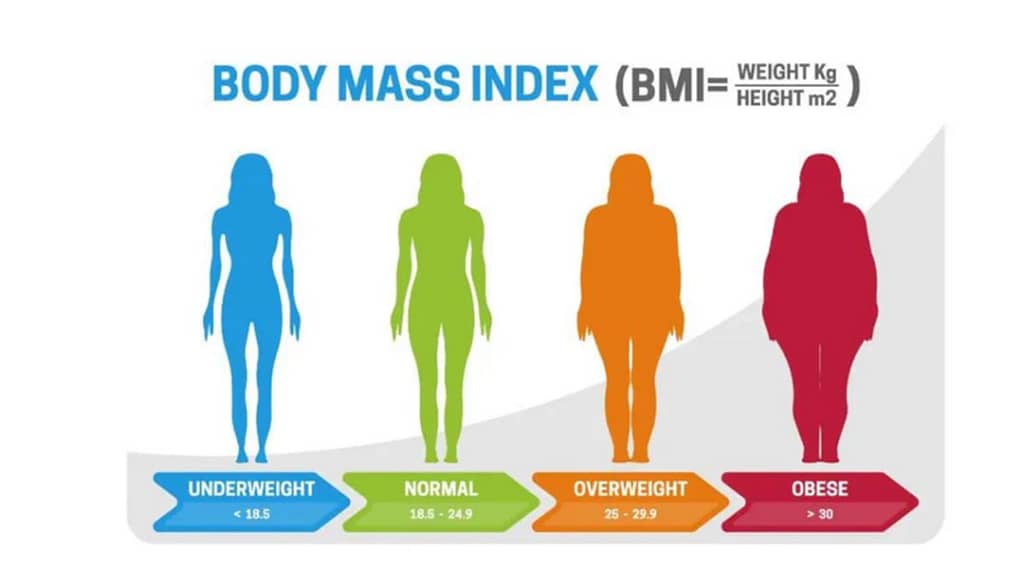
BMI = (Weight in kilograms) / (Height in meters)2
Alternatively, if using pounds and inches:
BMI = (Weight in pounds) / (Height in inches)2 x 703
Once calculated, the BMI value can be interpreted to determine a woman’s weight status category.
Interpreting BMI Results for Women
BMI values for women are categorized as follows:
Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
Obesity: BMI of 30 or higher
Importance of BMI for Health Insurance
The Body Mass Index (BMI) plays a significant role in health insurance for several reasons, outlined below:
- Risk Assessment: Insurers utilize BMI as a risk assessment tool to gauge an individual’s susceptibility to certain health conditions associated with weight, such as diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension.
- Premium Determination: In some cases, higher BMIs may result in elevated insurance premiums due to the increased risk of potential health issues and associated medical expenses.
- Underwriting Decisions: BMI may influence underwriting decisions, affecting coverage eligibility and terms. Individuals with higher BMIs may face stricter underwriting criteria or exclusions for certain conditions.
- Pre-existing Condition Consideration: Health insurance policies often consider obesity or related health conditions as pre-existing conditions, impacting coverage and reimbursement for associated medical treatments.
- Wellness Programs: Insurers may offer wellness programs aimed at managing weight and improving overall health for individuals with higher BMIs. These programs can incentivize healthy behaviors through discounts or rewards.
- Policy Benefits: BMI may affect the scope of coverage and benefits provided by health insurance policies, with some plans offering specific coverage for weight management programs, bariatric surgery, or obesity-related treatments.
- Long-term Health Management: Tracking BMI allows insurers to monitor policyholders’ health over time, facilitating early intervention and preventive measures to mitigate health risks associated with obesity.
In summary, BMI serves as a vital metric for health insurers, informing risk assessment, premium determination, underwriting decisions, and the design of wellness programs aimed at promoting healthier lifestyles and managing long-term health risks.
Tips for Women to Maintain a Healthy BMI
Maintaining a healthy BMI is essential for overall health and well-being. Here are some practical tips for women to achieve and maintain a healthy BMI:
- Balanced Diet: Consume a balanced diet consisting of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to support overall health and weight management.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, to maintain a healthy weight and improve cardiovascular health.
- Portion Control: Practice portion control and mindful eating to avoid overeating and manage calorie intake effectively.
- Stress Management: Incorporate stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to prevent emotional eating and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Schedule regular health check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your BMI, assess your overall health, and address any concerns or risk factors.
By understanding and monitoring their BMI, women can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy weight, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and improve overall well-being.
Additionally, recognizing the relevance of BMI in the context of health insurance can help women make informed decisions about their coverage and premiums, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes.