New Delhi: The stock market is a constantly evolving system heavily influenced by various factors. One of the most significant factors is the behaviour of the investors who participate in it. Behavioural finance is a field of study that seeks to understand how human behaviour and emotions impact financial decision-making and the stock market’s performance.
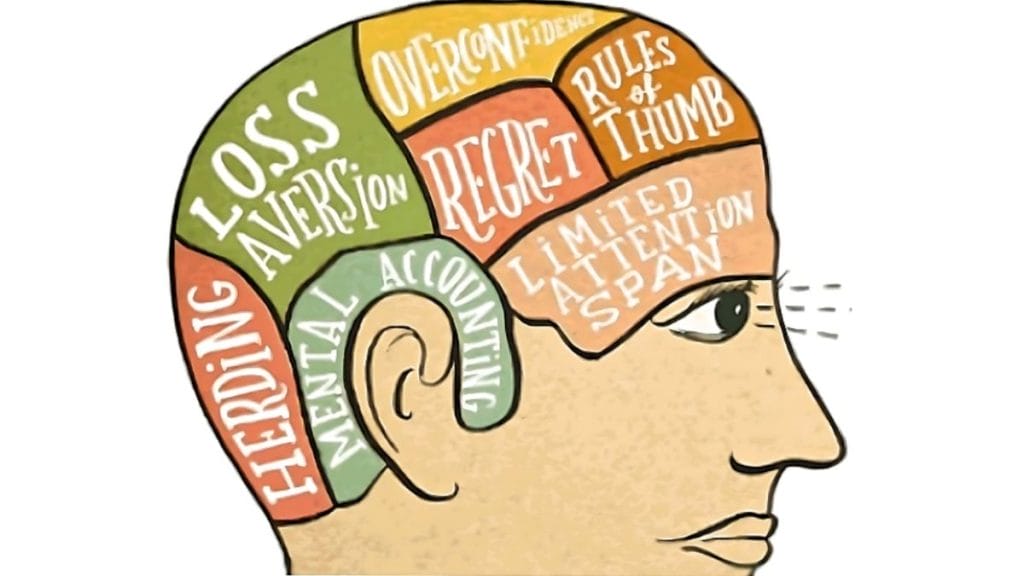
Traditional finance theories assume that investors are rational and will always make decisions based on objective data and analysis. However, behavioural finance theory challenges this view by recognizing that investors are not always rational and can be influenced by a variety of factors that have little to do with the underlying fundamentals of a particular stock or company. These factors can include emotions, cognitive biases, and herd behaviour.
One of the most significant aspects of behavioural finance is the concept of herd behaviour. This occurs when investors follow the actions of others rather than making decisions based on their own analysis. This can lead to situations where a stock becomes overvalued as investors are willing to pay more than its intrinsic value. Eventually, the market will correct itself, and the stock will experience a significant drop in value. This can lead to substantial losses for investors who follow the herd mentality.
Another important aspect of behavioral finance is cognitive biases. These are systematic errors in thinking that can lead to irrational decision-making. For example, confirmation bias occurs when investors only seek information confirming their beliefs rather than considering all available evidence. This can lead to poor investment decisions and significant losses.
Overconfidence bias is another cognitive bias that can impact the stock market. This occurs when investors are overly confident in their ability to predict future events or market trends. As a result, they may take on more risk than is necessary, leading to losses if their predictions do not materialize.
Emotions also play a significant role in the stock market. Fear and greed are two emotions that can drive investors to make irrational decisions. For example, during times of market volatility, fear can lead investors to panic and sell their stocks, even if they are still fundamentally sound. On the other hand, greed can cause investors to take on excessive risk in the pursuit of high returns, which can lead to significant losses if the market turns against them.
The availability heuristic is another concept from behavioral finance that can impact the stock market. This refers to the tendency for people to rely on the information that is most readily available to them, rather than seeking out all the relevant data. In the context of the stock market, this can lead to investors making decisions based on recent news or events, rather than taking a longer-term view. For example, if there is a string of positive news about a particular company, investors may be more likely to buy its stock, regardless of its long-term prospects.
So, what can investors do to mitigate the impact of behavioral finance on their investment decisions? Firstly, it is important to recognize the role of emotions and biases in investment decisions. By understanding these influences, investors can make more rational and informed choices. Additionally, it is important to take a long-term view of investments rather than making decisions based on short-term fluctuations in the market.
Investors can also benefit from diversifying their portfolios, which can help to reduce risk and exposure to individual companies or sectors. This can help to mitigate the impact of irrational decisions or market volatility.
Furthermore, investors can seek the advice of financial professionals who are trained to recognize and mitigate the impact of behavioral finance on investment decisions. Financial advisors, like INVasset Portfolio Managers, can provide objective analysis and help investors make informed decisions not based on emotions or cognitive biases.
INVasset’s model is based on Algorithmic investing, also known as quantitative investing, which uses computer algorithms to make investment decisions. These algorithms are designed to analyze large amounts of data and identify patterns and trends in the market. By doing so, algorithmic investing can help overcome behavioural anomalies in the stock market that can lead to irrational and emotional decision-making by human investors.
Here are a few ways how INVassset AAID overcomes behavioural anomalies in the stock market
1. Removing emotions: One of the biggest challenges for human investors is controlling their emotions when making investment decisions. Fear and greed can lead to irrational decisions that can be detrimental to a portfolio. INVasset AAID removes emotions from the decision-making process by using data and statistical models to make investment decisions.
2. Consistency: Another challenge for human investors is consistency. Even the most disciplined investors can have bad days, leading to poor investment decisions. INVasset AAID is designed to be consistent, making investment decisions based on pre-defined rules and criteria. This consistency helps avoid emotional biases and impulsive decision-making.
3. Speed of Change: In the stock market, trends change frequently based on various factors, and human investors can struggle to keep up due to recency bias. AAID can process vast amounts of data and make investment decisions much faster than humans, allowing investors to take advantage of market opportunities and avoid potential losses.
4. Backtesting: One of the advantages of INVasset AAID is the ability to backtest investment strategies using historical data. INVasset AAID has backtested data for the past 3 decades, covering over 5 stock market cycles. This data has enabled INVasset to develop a balanced alpha-creating strategy and reduce the risk of making decisions based on biases or emotions.
5. Diversification: INVasset AAID also helps to diversify portfolios by identifying investment opportunities across different sectors and asset classes based on numerous valuation factors.